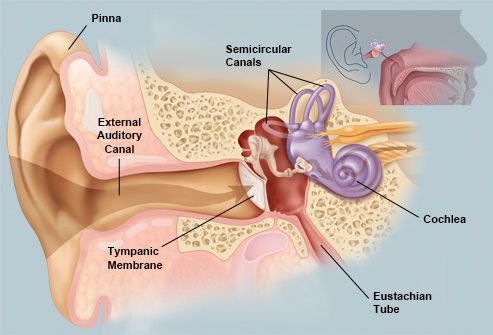
 The ear is divided into three divisions: Outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear consists by the pinna and the auditory canal. Pinna is the flap of cartilage that focus the sounds vibrations into the ear. The auditory canal is a pathway that amplifies the sound, as well as prevent the ear from infections due to its hair.
The ear is divided into three divisions: Outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear consists by the pinna and the auditory canal. Pinna is the flap of cartilage that focus the sounds vibrations into the ear. The auditory canal is a pathway that amplifies the sound, as well as prevent the ear from infections due to its hair.The middle ear is formed by the tympanum, ossicles and the oval window. The tympanum, also called eardrum, transforms the sound waves into mechanical energy, and passed to tiny bones called ossicle. This bones amplifies the sound a lot. They are: Hammer, anvil and stirrup.
The ear also count with a tube that connects the tongue and the ear. The Eustachian tube works to equalize the pressure in the ears.
The inner ear consists of three structures: the semicircular canals, the vestibule, and the cochlea.
The cochlea is used for hearing. It is within the cochlea that mechanical energy turns into electochemical impulses and are translated by the nervous system. The cochlea is filled with fluid. Wen the oval window vibrates, waves a made.
In the middle of Cochlea, there is the organ of Corti, which is known as the organ for hearing. Along the base of the organ of Corti, there is the basilar membrane, which is the location of the hair cells, that have structures called stereocilia. The end of the stereocilia are attached to the tectorial membrane. When the waves hit the basilar membrane, it goes up and down, bending the streocillia, that will be felt by the hair cells that will send a neural impulse to the brain.
Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário