- Embryonic period of development: This period of development takes place in the first two third of the first trimester, which means the first 8 weeks. During this time, cells are been divided and tissues and organs are been formed, as well as structures that support and nourish the developing embryo.
- Fetal period of development: This period starts in the ninth month until the birth. During the fetal period, the body growth rapidly and organs start to work, formatting organ systems.
Fertilization
Fertilization is the starting point of the human development. It involves the joining of male and female gametes to form a single cell that have 46 chromosomes, 23 from each parent.
 In the female body, after the egg is release of the follicle, thanks to the hormone LH, it start its journey to the uterus in the oviduct, with the help of muscular contractions and the wavelike movements of the scilia, that lines in the walls of the oviduct. It takes about four days to reach the uterus, so the egg needs to be fertilized in this period of time.
In the female body, after the egg is release of the follicle, thanks to the hormone LH, it start its journey to the uterus in the oviduct, with the help of muscular contractions and the wavelike movements of the scilia, that lines in the walls of the oviduct. It takes about four days to reach the uterus, so the egg needs to be fertilized in this period of time.
Millions of sperms get into the vagina, they need to survive a long path until reach the ovum. Some die due to acid in the vagina, or because of the female's immune system, some however, take the wrong way.
The ovum is protected by a membrane that also provides it energy. In order to penetrate this membrane, the sperm cells come with the acrosome, that have enzymes. Hundreds of sperm are necessary to make a pathway through the membrane, that's why the first sperm to reach the ovum, is not always the first one to get inside it. Once one sperm cells get inside, the membrane of the ovum depolarize and prevent the other perms to get in.
As time passes by the genetic material of the gametes mix and his result in the formation of a zygote.
Cleavage
 As the egg is being fertilized, it keeps moving in the oviduct. During the journey to the uterus, many events can be observed in the zygote.
As the egg is being fertilized, it keeps moving in the oviduct. During the journey to the uterus, many events can be observed in the zygote.
In short period of time, the zygote start to divide into different numbers of cells. It divides so fast that the size of the zygote remains the same. The process of division without the enlargement of the cells is called cleavage.
When the number of cells reach 16, the zygote is now called morula. When the morula reaches the uterus it starts to be filled by liquid from uterus. As the fluids gets in the embryo, it start a formation of two different group of cells.
The entire structure is called blastocyst. One group of cells called trophoblast forms the outer layer of the blastocyst. The trophoblast will form a membrane called chorion, that will become part of the placenta.
The other group of cells are called the inner cell mass, or embryoblast. They will develop in the embryo.
 The balstocyst will attach to the endometrium, with the inner cell mass against it. The trophoblast will secrete enzymes that digest some of the tissues and blood vessels of the endometrium. In a process called implatation, the blastocystslowly sinks into the endometrium. After this process is done, the woman is said to be pregnant.
The balstocyst will attach to the endometrium, with the inner cell mass against it. The trophoblast will secrete enzymes that digest some of the tissues and blood vessels of the endometrium. In a process called implatation, the blastocystslowly sinks into the endometrium. After this process is done, the woman is said to be pregnant.
About the time that the implantation occurs, the trophoblast starts to secret the hormone hCG. This hormone has the same function as the LH. It maintains the corpus luteum alive, that will keep the level of estrogen and progesterone high, which will prevent the endometrium to be broken down. After a couple of months, the corpus luteum can be degenerated, since the placenta can secret enough estrogen and progesterone by its own.
Tissue Formation
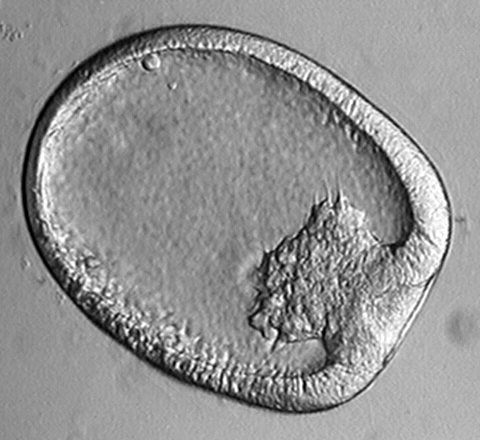 When the process of implantation is completed, the inner mass cell starts to change. A space starts to be formed between the trophobalst and the inner mass cells. This space is called amniotic cavity, and will soon be filled with fluid, which the embryo will be floated in.
When the process of implantation is completed, the inner mass cell starts to change. A space starts to be formed between the trophobalst and the inner mass cells. This space is called amniotic cavity, and will soon be filled with fluid, which the embryo will be floated in.
As the amniotic cavity forms, the inner mass cells start to from a disk, called the embryonic disk. The embryonic disk is formed by three layer: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. These are called the primary germ layers, and the process of their formation is called gastrulation. The disk is naw called gastrula.
The ectoderm will form our skin, nervous tissue, teeth, eye lens, and etc. The mesoderm will form the blood vessels, muscles tissues, bones, heart and etc. The endoderm will form the respiratory and digestive tract, among other structures.
Gastrulation marks the initiation of the morphogenesis, that is the series of events that form distinct structures of the developing organism. Differentiation is the cellular process which enables the cells to develops in a certain shape and perform a certain function.
Organ Formation
After the 8 week, 90% of the organs are formed, and the embryo can now be called fetus.
Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário